Michael Hudson on Ukrainian Sanctions with Rosss Aschroft
Ross [00:00:29] Welcome to Renegade Inc. Whatever the outcome in Ukraine, one thing is for sure the economic reverberations will be felt by everyone for years to come as the world divides between the West and a rapidly reshaping Eurasia.
Ross [00:00:49] Michael Hudson, always a pleasure to have you on the programme, welcome to Renegade Inc.
Michael Hudson [00:00:53] Thank you for inviting me.
Ross [00:00:55] Michael, sanctions, sanctions, sanctions is all we hear now. We’re sanctioning people. The West sanction people back to the Stone Age. What are the unintended consequences of sanctions?
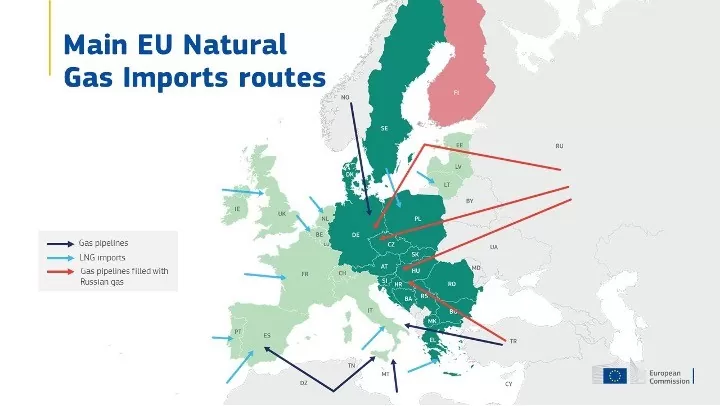
Michael Hudson [00:01:05] Well, one is to serve very much like a protective tariff on the sanctioned country. For instance, when America made sanctions on European trade with Russia, Lithuania dutifully stopped exporting cheese to Russia. Well, the result is that Russia set up its own cheese’s sector, and now it’s self-sufficient in cheese. If you sanction a country, you force it to become more self-reliant and across the board, from agriculture to dairy products to technology, Russia is forced to become more self-reliant and at the same time to depend much more on trade with China for the things that it is still not self-reliant in. So America is bringing about exactly the opposite of what it intended. It’s hopeless to somehow isolate Russia and then be able to go after China without Russia. And instead, what it’s doing is integrating the Eurasian core, Russia and China, exactly the policy that Henry Kissinger warned against going all the way back to Mackinder a century ago that said, Eurasia is the world island, Russia and China could be the whole world centre. That’s what the fight is all about. Well, American sanctions are driving Russia and China together, and America has gone to China and said, Please don’t support Russia. It most recently, on Monday, March 14, Jake Sullivan came out and told China, we will sanction countries that break our sanctions against Russia. And basically, China said, fine. You know, we’ll just break off all the trade between East and West now and the East, Eurasia is pretty much self-sufficient. The West is not self-sufficient since it began to industrialise, and it’s heavily dependent on Russia for not only oil and gas, but palladium and many raw materials. So the sanctions are ending up driving a wedge between the European countries.
Ross [00:03:31] Don’t people who apply these sanctions think this through? Are they so short-sighted they don’t understand that these sanctions are going to build further capacity within Russia, push Russia further towards China, make that economic alliance concrete and, ultimately, you’re not going to be able to keep the lights on in in Europe? All the while underestimating the fact that from a food security point of view – take the U.K., for instance, a net importer of food – not appreciating the fact that, for instance, Russia/Ukraine, they create twenty five percent, a quarter, of all wheat annually. The estimation this year is one hundred and two million tonnes Russia and Ukraine, wheat. Don’t people realise that there’s going to be a massive knock on effect?
Michael Hudson [00:04:23] Yes, they do realise it. Yes, they’ve thought it all through. I worked with these people for more than 50 years.
Ross [00:04:31] Who are these people?
Michael Hudson [00:04:32] The neocons, basically, the people who are in charge of U.S. foreign policy? Victoria Nuland and her husband, Robert Kagan, the people that President Biden has appointed all around him, from Blinken to Sullivan and right down the line. They are basically urging people around the New American Century. They’re the people who said America can run the whole world and create its own reality. And yes, they know that this is going to cause enormous problems for Germany. They know that not only will it block the energy that Germany and Italy and other countries in Europe need through their oil and gas, but also it’ll block the use of gas for fertiliser, upping their fertiliser production and decreasing their food production. They look at this and they say, How can America gain from all of this? There’s always a way of gaining what something looks to be bad. Well, one way they’ll gain is oil prices are going way up. And that benefits the United States whose foreign policy is based very largely on oil and gas. The oil industry controls most of the world’s oil trade, and that explains a lot of the US diplomacy. This is a fight to lock the world energy trade into control by U.S. companies, excluding not only Iran and Venezuela, but also excluding Russia.
Ross [00:06:16] So as Europe pushes towards more and more green and renewable energy and this for the Americans they must think it’s a dreadful scenario insofar as they can’t sell the oil as Europe becomes or wants to become more self-sufficient. So ultimately, and Britain net zero, whatever that means. But but going down the renewables path, going down the solar path takes America’s dependency or dependency on America out the game, doesn’t it?
Michael Hudson [00:06:49] This is exactly the point that the European public has not realised. While most of the European public wants to prevent global warming and prevent carbon into the atmosphere, U.S. foreign policy is based on increasing, and even accelerating, global warming, accelerating carbon emissions because that’s the oil trade. Suppose that Europe got its way. Suppose if the Greens got what they wanted and Germany and Europe were completely dependent on solar energy panels, on wind energy and to some extent, on nuclear power, perhaps? Well, if they were completely self-sufficient in energy without oil or gas or coal, America would lose the primary lever. It has over the ability to turn off the power and electricity and oil of any country that didn’t follow U.S. diplomatic direction.
Ross [00:07:48] So when we take your analysis here and we think about how the sanctions are going to build capacity, push Russia and China together, when we start to look at sort of piggy in the middle, if you like the EU, when we’re thinking about America, the EU has had a sort of abusive relationship with the Americans for quite some time now, hasn’t it?
Michael Hudson [00:08:06] Well, that’s that’s true in the sense that EU foreign policy has basically been turned over to NATO. So instead of European voters and politicians making their policy, they’ve relinquished European foreign policy to NATO, which is really an arm of the US military. So yes, Europe has had a decent relationship with the United States diplomatically by saying yes, yes, please or yes, thank you by not being independent. Of course, if it were independent, the relationship would not be so friendly and decent.
Ross [00:08:46] So for countries that are net importers of food, need to keep the lights on, need heating and need cheap oil. How does this pan out? What does it look like for the UK? What does it look like for the EU?
Michael Hudson [00:08:59] Well, Vice President, Kamala Harris the other day said to Americans, Yes, life is going to be much more expensive. Our oil prices are going up and squeezing families. But think of the poor Ukrainian babies that we’re saving. So take it on the chin for the Ukrainian babies. So basically the United States is presenting horror stories of the Ukraine and saying, if you don’t willingly suffer now by isolating Russia, then Russia is going to roll over you with tanks just like it rolled over Central Europe after World War Two. I mean, it’s waving the flag of Russian aggression, as if Russia or any country in today’s world has an army that’s able to invade any other industrial nation. All military can do today of any country is bomb and kill other populations and industrial centres. No nation is able to occupy or rollover any industrial country. And the United States keeps trying to promote this mythology that we’re still in the world of 1945. And that world ended really with the Vietnam War when the military draught ended. And no country is able to have a military draught to raise the army with necessary to fight to invade. Russia can’t do it any more than Europe or the United States could do it. So all the United States can do is wave warnings about how awful Russia is and somehow convince Europe to follow the US position. But most of all, it doesn’t really have to. Europe doesn’t really have a voice, and this is what the complaint by Putin and Foreign Secretary Lavrov have been saying. They say that Europe is just following the United States and it doesn’t matter what the European people want or what European politicians want. The United States is so deeply in control that they really don’t have much of a choice.
Ross [00:11:15] When does the consumer start to feel this? When does the European or British consumer start to feel the pinch when these sanctions are enacted? And what does that look like?
Michael Hudson [00:11:25] Well, it depends on how fast the sanctions work. The United States said ‘Well, in another year and a half, we’ll be able to provide Europe with liquefied natural gas’. Well, the problem is, first of all, they’re not the ports to handle the liquefied natural gas to go into Europe. Secondly, there are not enough ships and tankers to carry all of this gas to Europe. So unless there is very warm winters, Europe is not going to have a very easy time for the next few years. And that’s only for oil and gas. It’s dependent on raw materials that Russia produces. For instance, palladium is necessary for catalytic converters. Titanium is necessary to make the screws that are especially used on aeroplanes that are strong enough not to buckle and break when winds go up and down and when they’re full. Russia even produces the neon and the crypton that are necessary for making some kind of electronic uses and also for many components that go into computers and information technology. There’s a whole range of exports that Europe is highly dependent on, and the United States has provided Putin with a whole list of these exports, saying, Well, OK, we’re going to fight against Europe buying your oil and gas but you can certainly sell us your heavy oil that we need since we’re not buying it from Venezuela. We certainly need the following list of critical materials that we need, like helium and crypton. These are our pressure points. Please don’t press on them. Well, you can imagine what Putin and his advisers are saying. Thank you for giving us this list of the pressure points that you’re exempting from the trade sanctions. I think if you really want a break in the unilateral, unipolar world, I think we should break now and see whether you really want to get along without trading.
Ross [00:13:51] Michael Hudson, welcome back, second half, Renegade Inc. Wonderful to have you. In that first half we followed the money, if you like. We talked about sanctions and the unintended consequences. I just want to pull back a little further if we can and just talk about the sort of tectonic shifts that are going on in the world. I spoke to somebody from Russia recently and what he said was very straightforward. He said, now what we have to do is begin to learn to live without the West. Do you think that that sentiment is proliferating across Russia now? Is that the mindset?
Michael Hudson [00:14:22] Well, if you read President Putin’s speeches, that’s exactly what’s happening. And Secretary Lavrov has voiced exactly the same feeling. There’s almost a disgust with the West and a feeling from Putin, Lavrov and the other Russian spokesmen, how could we everhave hoped to have an integration with Europe after 1991? Europe really was not on our side at all, and we didn’t realise that Europe is really part of the U.S. diplomatic sphere. It’s like all of Europe is now backing the attack on Russia. The best to do is reorient our economy towards China, Asia and Eurasia and become our own self-sufficient, independent centre
Ross [00:15:15] De-dollarisation and the amassing of plenty of gold by both the Russians and the Chinese. Just talk us through that.
Michael Hudson [00:15:21] Well, Ross, you asked in the first half of this interview how has American sanctions worked against it? I should have mentioned what you just mentioned, the dollar. The United States just grabbed all of Russia’s foreign exchange reserves, just as England a few months ago grabbed all of Venezuela’s gold that was held in the Bank of England when Venezuela tried to spend this gold on buying medical supplies to cope with the COVID virus. So basically, the United States have said, if any foreign country holds its reserves in the United States or accounts in U.S. banks. If a country in the global south tries to pay its foreign debt by holding its reserves in US banks in order to be the paying agent on the interest on its foreign debt. And if that foreign country does something we don’t like, like trade with Russia or permit more labour unionisation or try to become independent in food, we’re just going to do what we did to Venezuela, what we did to Iran when we grabbed its foreign exchange reserves or what we did to Russia. And that means that other countries all of a sudden see what they thought was their flight to security, what they thought was their most secure savings, their holdings in U.S. banks, US treasury bill, all of a sudden, is holding them hostage and is a high risk. Even the Financial Times of London has been writing about this, saying, how can the United States that was getting a free ride off the dollar standard for the last 50 years, ever since 1971, when foreign countries held dollars instead of gold and basically holding dollars means you buy U.S. Treasury bonds to finance the US budget deficit and the balance of payments deficit. How can the United States kill the goose that’s giving it the free ride? Well, the answer is that other countries can only move into gold and there’s an alternative to the dollar because that’s something that all the countries of the world have agreed upon is an asset, not a liability. If you hold any foreign currency, that currency is a liability of a foreign country, and if you hold gold, it’s a pure asset. There’s no country that can cancel it, the Americans can’t cancel Russia’s gold supply that’s held in Russia, although it can grab Russian gold supply if it were to hold it in the New York Federal Reserve Bank or the Bank of England. So other countries are not only moving to gold, Germany is bringing its gold back from New York, the Federal Reserve, in aeroplanes back to Germany, so it’ll have its own gold just in case German politicians would do something the United States didn’t like and the United States would simply grab Germany’s gold. The United States sanctions, and it’s especially it’s grabbing on foreign reserve, has started a war that is dividing the world between the West and Eurasia.
Ross [00:18:40] A technical part to all of this because let’s face it, it is an information war and it’s also an economic war. Is it the FIRE sector that you point out – the financial, insurance and real estate sector. Is it that they want to continue the exorbitant privilege of credit creation, because ultimately, if you think about gold, there’s no counterparty risk. Gold is gold and it has been for millennia. Far from being a barbarous relic, by the way now, people are starting to realise the intrinsic value, especially as crypto falls apart. Can you just talk a little bit about this, the FIRE sector wanting the exorbitant privilege of creating credit?
Michael Hudson [00:19:19] This is really what the new world division and global fracture is all about. You’re right, Ross. If you look at after World War One, the American fight against Soviet communism, was basically a fight of industrial capitalism against the threat of socialism. But after 1991, and especially in the last two decades, America deindustrialised. So the fight is not by industrial capitalism against countries pushing their labour up. It’s a fight of neoliberalism against industrial capitalism or socialism abroad. It’s against industrial capitalism evolving into socialism. It’s a belief that, well, now that America’s be industrialised, how is it going to control the world economy? Well, it’ll control it through a financial means by being the creditor and foreign countries debt payments to America will enable it to make its military payments abroad and finance its trade deficit. But also, America’s purchase of key natural resources will give it natural resources when its purchase of takeover of real estate is going to essentially make the United States the landlord class and monopoly class, that mediaeval Europe had to hold the rest of the population in serfdom. That basically is the American strategy of neoliberalism fighting against countries that reject privatisation and financialization of their economy, and specifically financialization under the control of U.S. banks, U.S. private capital and allied satellite banks and capital from England or France or Germany. This is exactly the fight. Will banking and finance control the world economy or will other countries try to build up their own economies through labour and tangible capital formation?
Ross [00:21:27] Where do you stand on that? And I’m only asking you to predict the future, Michael. How do you think this plays out? Because the way you’ve depicted it is the rent seekers, the neoliberal rent seekers on one hand, and there are value creators on the other. And by the way, those two things don’t sit very well together, as we know. How does that play out?
Michael Hudson [00:21:51] Even though the United States is the largest debtor economy in the world, it’s a creditor vis-a-vis the global south and other countries and it uses its creditor position to take over their natural resources, real estate, oil and gas, mineral rights and public utilities and natural monopolies and that are being privatised in government infrastructure. It’s becoming basically the landlord monopoly class of the entire world. That’s the U.S. strategy, and that’s the key to why the world is fracturing globally. And in the past, the global south countries were unable to fight against this tendency in the 70s and 80s with the Vendome conference on. But now that China and Russia threatened to be a self-sufficient core in Eurasia, this is the great threat to the American dream of becoming a landlord and financier of the world.
Ross [00:22:50] How do you think this pans out?
Michael Hudson [00:22:52] Well, the question is whether the United States is if we can control the world, who wants to live in a world like that, let’s blow it up. The question is whether the United States will actually go to war. The only lever that it has left is to drop bombs and to destroy and make the world look like Ukraine. So from the U.S. point of view, Europe’s future and Eurasia’s future is the Ukraine. Look at what we will do to you if you don’t follow our policy. America has just moved al Qaeda very heavily in the Ukraine to sort of repeat in Ukraine and Europe what it was doing in Syria and Libya. And the United States says this is what we can do. What are you going to do about it? Do you really want to fight. But the rest of the world, certainly China and Russia says, Well, we’re ready to fight. So there is no telling what what you. And it comes down to personalities. Putin has said, well, do we really want to live in a world without Russia? If the United States is to attack us, we might as well end the world. The United States says, Do we really want to live in a world that we can’t control? If we’re not completely in control, we feel very insecure and we’re going to blow up the world. So you have this countervailing position in a world where all the arms control has been dismantled by the United States in the last few years. The United States has withdrawn from all of the agreements that Russia and China have tried to promote. And Europe is standing by and apparently is willing to be the sacrificial lamb in all of this as Ukraine is being the sacrificial lamb. So the United States and Russia say, let’s fight to the last European. And Russia initially didn’t want that because it was hoping that Europe and Russia would have a mutual gain in trade and investment relationships. But now it doesn’t feel that way. And there may be a proxy war between the United States over the European economy, not necessarily bombing Europe, but trade sanctions, energy sanctions, the kind of disruption that Europe is going to be seeing in the next year is if it loses Russian oil and gas and minerals and also, I think Chinese exports.
Ross [00:25:25] Is there a moment where cooler heads prevail and suddenly the West and other places realise that they’re dependent from a food security point of view, from an energy security point of view that we are dependent? And is there a moment at that point that you can thaw a frozen conflict by saying, actually, if we both meet, we just take a step toward each other, actually, we can do something in a collaborative way? Now I get what you’ve said throughout the rest of the programme, and I give this a percentage possibility of about three percent, but isn’t there a strategy to say, actually, we’ve had all the grandstanding, we’ve had all the brinksmanship, we should now sit around the table and try and work something out?
Michael Hudson [00:26:03] I don’t see any cooler heads in the United States. The surprising thing is that here it’s the right wing channel, the Republican Fox Channel, is the only channel that’s taking the anti-war stand and is saying we shouldn’t be at war in Ukraine. It’s the only channel that’s talking about here is how Russia sees the world. Do we really want to take a one sided perspective or do we want to see the actual dynamics at work? So it was the Republicans and the right wing that is now primarily against the NATO war in the Ukraine. The left wing seems to be all for it, but the left wing of the Democratic Party is in office and I don’t see any cooler heads in the Democratic Party at all. And I’ve known many of these people for many decades, and they are willing to go to war for a death. There are still back in the world of World War Two when the fight was against the Nazis and anti-Semitism. They’re still living in a kind of mythology world, not in the real world. And the thought that the world can come to an end either doesn’t have a reality to them or is Herman Cain said, Well, somebody is going to survive.
Ross [00:27:29] Michael Hudson always a pleasure, a great insight. And, you know, it’s just refreshing to hear such cut through. Thank you very much for your time.
Michael Hudson [00:27:38] Well, thank you very much for having me, Ross.