The death of Queen Elizabeth II, where the BBC dropped programming to run endless, wall-to-wall coverage, has underlined the fact to many Britons that the network is far from impartial, but the voice of the state.
The BBC website draped itself in black, printing stories such as “Death of Queen Elizabeth II: The moment history stops,” while BBC News presenter Clive Myrie explicitly dismissed the cost of living and energy crisis wracking the country as “insignificant” compared to the news.
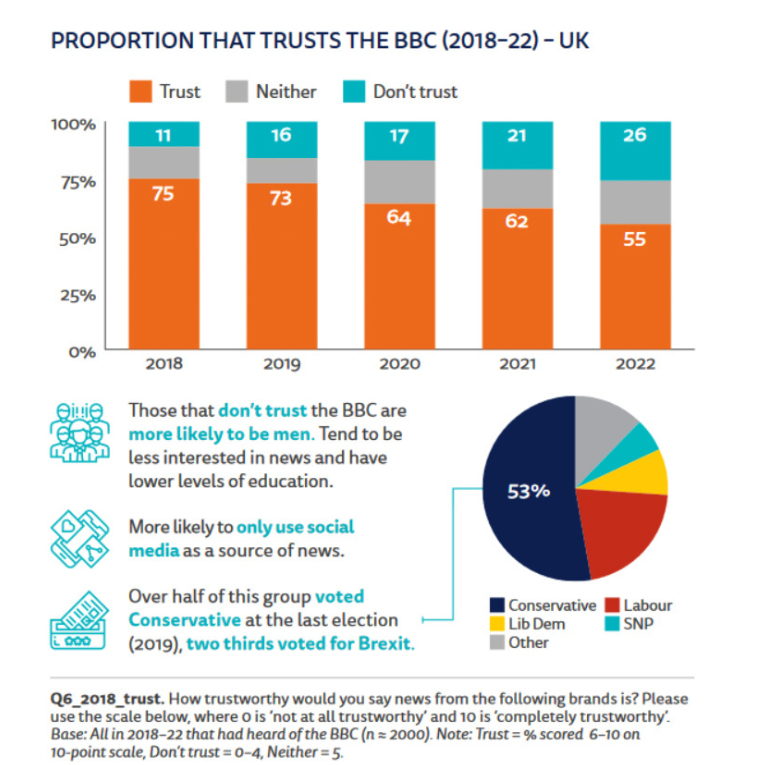
But even before the monarch’s death, the BBC’s reputation was in crisis. Between 2018 and 2022, the number of Britons saying they trusted its coverage dropped from 75% to just 55%. Yet it still remains a giant in media; more than three-quarters of the U.K. public rely on the network as a news source.
However, this investigation will reveal that the BBC has always been consciously used as an arm of the state, with the broadcaster openly collaborating with the U.K. military, the intelligence services and with NATO, all in an effort to shape British and world public opinion.
The BBC-to-NATO pipeline
The BBC has always cultivated a close relationship with the British military, despite the inherent journalistic conflicts of interest present. “In theory the BBC is supposed to hold power to account, but this is not how impartiality has tended to work in practice,” Tom Mills, an academic and author of “The BBC: Myth of a Public Service,” told MintPress, adding that “a certain deference is expected of you…It’s a structural feature of the organization, and to some extent journalism more broadly.”
Yet, studying employment databases and websites reveals the existence of a revolving door between the broadcaster and NATO.
Between 2007 and 2008, longtime BBC producer and news presenter Victoria Cook, for instance, was simultaneously collecting a paycheck from NATO, working as a journalist and media trainer.
Oana Lungescu, meanwhile, left her job as a correspondent at the BBC World Service (the broadcaster’s flagship international radio service) in 2010 to take a job as a NATO spokesperson.
Another BBC employee who went through the BBC-to-NATO-pipeline is Mark Laity, who left his position as the network’s defense correspondent to become the deputy spokesman to NATO Secretary General Lord Robertson – a man who journalistic ethics dictates Laity should have been closely scrutinizing, not doing public relations for him.
David McGee also left his role as a news producer for the BBC to work for NATO – in this case as a media manager, where he, in his own words, “Provided PR support to military and civilian stakeholders for external communications audience,” and, “Undertook crisis management of news events for [the] U.S. military.”
Others traveled the other way. One of them is Terence Sach, who left his job as an intelligence and security analyst at the U.K. Ministry of Defense in 2017 to become an information security specialist at the BBC.
Where news meets psyops
Perhaps most noteworthy, however, is the BBC’s employment of NATO psychological operations officers, tasking them to provide supposedly objective information while simultaneously moonlighting as propagandists for the military alliance.
Between 1994 and 2014, for example, Sulaiman Radmanish worked for the BBC World Service, primarily helping to produce content targeting the Afghan population. Over a similar time period (2005-2014), he worked as a video editor for NATO, “edit[ing] short Psyops clips” according to his LinkedIn profile. It is surely no coincidence that his work with both the BBC and NATO ended in the same year as Britain’s withdrawal from Afghanistan – a country it had been occupying since 2001.
This close relationship with the military continues to the present day. One example of this is the BBC’s newly appointed head of assurance, Khushru Cooper. According to his social media profile, Cooper continues to be a commissioned British Army officer – a post he has held for 20 years.
The myth of a left-wing bias
In August, top BBC news anchor Emily Maitlis caused a storm of controversy after she claimed that the network’s former head of political programming, Robbie Gibb, was, in her words, an “active agent of the Conservative party” who influenced politics coverage. Others agreed, including BBC media editor Amol Rajan, who said Gibb’s appointment “clearly strengthens the BBC’s links not just with Westminster, but with the Conservative Party specifically”.
At the time she made the remarks, Maitlis had recently resigned, although only after she had come under huge pressure for reporting on how senior Conservative politicians were blatantly flouting their own COVID-19 lockdown rules.
Richard Sharp, the BBC’s chairman, insisted that Maitlis was “completely wrong”. “We cherish the editorial independence of the BBC,” he added. Yet her claims were hardly outlandish. Robbie Gibb is the brother of Tory MP and former cabinet minister Nick Gibb, and left the BBC in 2017 to become Director of Communications for Conservative Prime Minister Theresa May. And Sharp himself was an advisor to senior Tories, including Chancellor Rishi Sunak and future Prime Minister Boris Johnson. He is also one of the party’s largest benefactors, donating at least £400,000 to its coffers.
Many of the BBC’s biggest and most influential names also have similar connections to conservative power. Tim Davie, the corporation’s director general, was the deputy chairman of the Hammersmith and Fulham Conservative Party and stood for election as a Tory on two occasions. Nick Robinson, the BBC’s former political editor and current host of its flagship Today program, was chairman of the National Young Conservatives and president of the Oxford University Conservative Association. And Andrew Neil, a longtime senior politics presenter at the BBC, was far-right media baron Rupert Murdoch’s right-hand man and the chairman of the hard-right Spectator magazine.
This glut of right-wingers in top jobs is not matched by an equal number on the left. Far from it. In fact, from the earliest days of the BBC, the secret services have vetted the majority of its staff – even for minor positions – in order to ensure that those it deems too left-wing, radical or anti-war will never enter its ranks. This practice continued until at very least the 1980s. However, when BBC journalists asked the company in 2018 whether this practice is still ongoing, they refused to answer, citing “security issues” – a response many took to be a tacit “yes”.
Much of this sentiment is driven by the Conservative Party itself, which constantly harangues the BBC over what it claims is an anti-Tory bias, to the point where the current government under Liz Truss have vowed to pull all its funding, effectively destroying it. Earlier this week, Home Secretary Suella Braverman claimed that there has been a “march of socialism” throughout public life and that there was an “urgent need” to address the balance by placing right-wingers into more positions of power.
The BBC is not financed by advertising, but from a license fee paid for by all Britons (with some exceptions) who wish to have a television. The cost of the license – and therefore the budget of the BBC – is set by the government, giving it a weapon to use against the corporation.
As former Director of BBC personnel, Michael Bett said,
The license fee became a bigger and bigger political issue. Therefore, it mattered very much what the government thought about you, and you couldn’t rely on the general reputation. You had to please the government.”
“The BBC is essentially a state broadcaster with a high degree of operational autonomy. It’s reporting isn’t directed by government, or by any department of state…plus its public income comes from outside of general taxation,” Mills told MintPress, adding:
But governments control that income, they appoint executives to its board and they periodically define its terms of operations. Ultimately it is answerable to governments and this is well understood in the BBC itself. They are very conscious of how they are perceived by politicians.”
Voice of the state
The work of Mills and others charting the history of the British Broadcasting Corporation has underlined the point that, from its very inception, it has been fundamentally intertwined with British state power, helping to promote and preserve it at home and abroad.
The BBC was established in October 1922 to take advantage of emerging radio technology, and played a key role in the U.K. General Strike of 1926. 1920s Europe was an extremely turbulent time, as class war, revolution and socialism had come to the fore. In 1917, Russia had overthrown its czar and brought Lenin’s Bolshevik party into power, only to be immediately invaded by Britain, the United States and other powers in an attempt to “strangle Bolshevism in its cradle” as Winston Churchill put it.
The German uprisings of 1917 and 1919 had ended the First World War and led to the fall of the monarchy. Closer to home, Ireland had fought its way to independence from Britain. Meanwhile, in 1922, a communist uprising in Scotland had come close to sparking a revolution across the country.
These actions deeply troubled BBC chief Lord John Reith. And so when the Trades Union Congress called a general strike in 1926, the Scottish aristocrat offered his organization’s services to the Conservative government. The BBC became a “vital instrument of propaganda for a government determined to break the strike,” in Mills’ words, putting out non-stop propaganda demonizing the strikers and banning broadcasts from the Labour Party.
After the strike was broken, Reith proudly announced to listeners,
You have heard the messages from the king and the prime minister. It remains only to add the conviction that the nation’s happy escape has been in large measure due to a personal trust in the prime minister.”
Reith would later say that the BBC “saved” Britain and quipped that if France had had a state broadcaster in 1789, “there would have been no French Revolution.”
The government has long internally debated what its precise relationship with the BBC should be. Winston Churchill was in favor of officially taking over the corporation. However, others in government argued that it should be kept at arm’s length; that it would hold more persuasive power if it maintained a facade of independence. This was the approach Lord Reith favored, commenting that the government “know that they can trust us not to be really impartial”.
The enemy within
True to Reith’s vision, the BBC has maintained its role as state broadcaster and has functioned as one of the British establishment’s most potent tools in destroying any threat to its power and prestige. As Greg Dyke, BBC secretary general between 2000 and 2004 stated, the organization “helps maintain an unequal political system by being part of a Westminster conspiracy. They don’t want anything to change. It’s not in their interests.”
This was seen in full effect in the 1980s during the Miners’ Strike, where the BBC put out round-the-clock propaganda to help the Conservative Thatcher government defeat the strikers, going so far as to doctor footage to make it appear that miners had attacked the police, when, in fact, the opposite was the case.
Nevertheless, the Thatcher government’s attack on the BBC was fierce. Following the commissioning of Duncan Campbell’s series “Secret Society”, which exposed the existence of spy satellites that even parliament was not told about, the security services raided BBC offices in Glasgow and banned its publication.
More recently, when Scotland faced an independence referendum in 2014, the BBC published a torrent of negative stories on the issue, warning Scots that ruination awaited them if they chose to break away. This came to be dubbed “Project Fear” by detractors. Studies showed a clear quantitative bias towards anti-independence sources, with BBC presenters displaying open contempt or even hatred towards Scottish First Minister Alex Salmond.
Likewise, when Jeremy Corbyn became leader of the Labour Party, the BBC immediately trained its guns on him, constantly attacking and slandering him, implying he was a terrorist sympathizer, an antisemite, and a national security threat. After strong public pushback to its reporting, the BBC eventually investigated itself and concluded its own political editor, Laura Kuenssberg, had breached its impartiality and accuracy standards when covering Corbyn. Despite this, senior BBC figures still publicly maintain that the idea the organization was biased against him is “risible.”
Feature photo | Illustration by MintPress News
Alan MacLeod is Senior Staff Writer for MintPress News. After completing his PhD in 2017 he published two books: Bad News From Venezuela: Twenty Years of Fake News and Misreporting and Propaganda in the Information Age: Still Manufacturing Consent, as well as a number of academic articles. He has also contributed to FAIR.org, The Guardian, Salon, The Grayzone, Jacobin Magazine, and Common Dreams.



