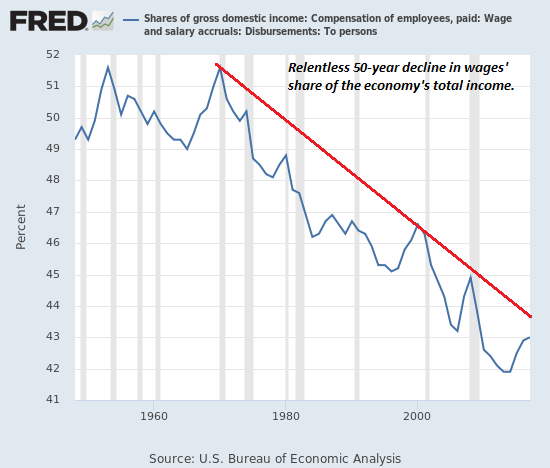
Sergey Karaganov argues Moscow is taking a new tack with the West, and is increasingly resistant to sanctions and political pressure
Moscow’s confrontation with NATO is just the start
It seems like Russia has entered a new era of its foreign policy – a ‘constructive destruction’, let’s call it, of the previous model of relations with the West. Parts of this new way of thinking have been seen over the last 15 years – starting with Vladimir Putin’s famous Munich speech in 2007 – but much is only just becoming clear now. At the same time, lackluster efforts to integrate into the western system, while maintaining a doggedly defensive attitude, has remained the general trend in Russia’s politics and rhetoric.
Constructive destruction is not aggressive. Russia maintains it isn’t going to attack anyone or blow them up. It simply doesn’t need to. The outside world provides Russia with more and more geopolitical opportunities for medium-term development as it is. With one big exception. NATO’s expansion and formal or informal inclusion of Ukraine poses a risk to the country’s security that Moscow simply won’t accept.
For now, the West is on course to a slow but inevitable decay, both in terms of internal and external affairs and even the economy. And this is precisely why it has started this new Cold War after almost five hundred years of domination in world politics, the economy, and culture. Especially after its decisive victory in the 1990s to mid-2000s. I believe [1] it will most likely lose, stepping down as the global leader and becoming a more reasonable partner. And not a moment too soon: Russia will need to balance relations with a friendly, but increasingly more powerful China.
Presently, the West desperately tries to defend against this with aggressive rhetoric. It tries to consolidate, playing its last trump cards to reverse this trend. One of those is trying to use Ukraine to damage and neuter Russia. It’s important to prevent these convulsive attempts from transforming into a full-fledged standoff and to counter the current US and NATO policies. They are counterproductive and dangerous, though relatively undemanding for the initiators. We are yet to convince the West that it is only hurting itself.
Another trump card is the West’s dominating role in the existing Euro-Atlantic security system established at a time when Russia was seriously weakened following the Cold War. There’s merit in gradually erasing this system, primarily by refusing to take part in it and play by its obsolete rules, which are inherently disadvantageous to us. For Russia, the western track should become secondary to its Eurasian diplomacy. Maintaining constructive relations with the countries in the western part of the continent may ease the integration into Greater Eurasia for Russia. The old system is in the way, though, and so it should be dismantled.
The critical next step to creating a new system (aside from dismantling the old one) is ‘uniting the lands’. It’s a necessity for Moscow, not a whim.
It would be nice if we had more time to do this. But history shows that, since the collapse of the USSR 30 years ago, few post-Soviet nations have managed to become truly independent. And some may never even get there, for various reasons. This is a subject for a future analysis. Right now, I can only point out the obvious: Most local elites don’t have the historical or cultural experience of state-building. They’ve never been able to become the core of the nation – they didn’t have enough time for this. When the shared intellectual and cultural space disappeared, it hurt small countries the most. The new opportunities to build ties with the West turned out to be no replacement. Those who have found themselves at the helm of such nations have been selling their country for their own benefit, because there’s been no national idea to fight for.
The majority of those countries will either follow the example of the Baltic states, accepting external control, or continue to spiral out of control, which in some cases may be extremely dangerous.
The question is: How to ‘unite’ the nations in the most efficient and beneficial way for Russia, taking into account the tsarist and Soviet experience, when the sphere of influence was extended beyond any reasonable limits and then kept together at the expense of core Russian peoples?
Let’s leave the discussion about the ‘unification’ that history is forcing on us for another day. This time, let’s focus on the objective need to make a tough decision and adopt the ‘constructive destruction’ policy.
The milestones we passed
Today, we see the inception of the fourth era of Russia’s foreign policy. The first one started in the late 1980s, and it was a time of weakness and delusions. The nation had lost the will to fight, people wanted to believe democracy and the West would come and save them [2]. It all ended in 1999 after the first waves of NATO expansion, seen by Russians as a backstabbing move, when the West tore apart what was left of Yugoslavia.
Then Russia started to get up off its knees and rebuild, stealthily and covertly, while appearing friendly and humbled. The US withdrawing from the ABM Treaty signaled its intention to regain its strategic dominance, so the still broke Russia made a fateful decision to develop weapon systems to challenge American aspirations. The Munich speech, the Georgian War, and the army reform, conducted amid a global economic crisis that spelled the end of the western liberal globalist imperialism (the term coined by a prominent expert on international affairs, Richard Sakwa) marked the new goal for Russian foreign policy – to once again become a leading global power that can defend its sovereignty and interests. This was followed by the events in Crimea, Syria, the military build-up, and blocking the West from interfering in Russia’s domestic affairs, rooting out from the public service those who partnered with the West to the disadvantage of their homeland, including by a masterful use of the West’s reaction to those developments. As the tensions keep growing, looking up to the West and keeping assets there becomes increasingly less lucrative.
China’s incredible rise and becoming de-facto allies with Beijing starting in the 2010s, the pivot to the East, and the multidimensional crisis that enveloped the West led to a great shift in political and geoeconomic balance in favor of Russia. This is especially pronounced in Europe. Only a decade ago, the EU saw Russia as a backward and weak outskirts of the continent trying to contend with major powers. Now, it is desperately trying to cling to the geopolitical and geoeconomic independence that is slipping through its fingers.
The ‘back to greatness’ period ended around 2017 to 2018. After that, Russia hit a plateau. The modernization continued, but the weak economy threatened to negate its achievements. People (myself included) were frustrated, fearing that Russia once again was going to “snatch defeat from the jaws of victory.” But that turned out to be another build-up period, primarily in terms of defense capabilities.
Russia has gotten ahead, making sure that for the next decade, it will be relatively invulnerable strategically and capable of “dominating in an escalation scenario” in case of conflicts in the regions within its sphere of interests.
The ultimatum that Russia issued to the US and NATO at the end of 2021, demanding they stop developing military infrastructure near the Russian borders and expansion to the east, marked the start of the ‘constructive destruction’. The goal is not simply to stop the flagging, albeit really dangerous inertia of the West’s geostrategic push, but also to start laying the foundation for a new kind of relations between Russia and the West, different from what we settled on in the 1990s.
Russia’s military capabilities, the returning sense of moral righteousness, lessons learned from past mistakes, and a close alliance with China could mean that the West, which chose the role of an adversary, will start being reasonable, even if not all the time. Then, in a decade or sooner, I hope, a new system of international security and cooperation will be built that will include the whole Greater Eurasia this time, and it will be based on UN principles and international law, not unilateral ‘rules’ that the West has been trying to impose on the world in recent decades.
Correcting mistakes
Before I go any further, let me say that I think very highly of Russian diplomacy – it’s been absolutely brilliant in the past 25 years. Moscow was dealt a weak hand but managed to play a great game nevertheless. First, it didn’t let the West ‘finish it off’. Russia maintained its formal status of a great country, retaining permanent membership in the UN Security Council and keeping nuclear arsenals. Then it gradually improved its global standing by leveraging the weaknesses of its rivals and the strengths of its partners. Building a strong friendship with China has been a major achievement. Russia has some geopolitical advantages that the Soviet Union didn’t have. Unless, of course, it goes back to the aspirations of becoming a global superpower, which eventually ruined the USSR.
However, we shouldn’t forget the mistakes we’ve made so we don’t repeat them. It was our laziness, weakness, and bureaucratic inertia that helped create and keep afloat the unjust and unstable system of European security that we have today.
The beautifully-worded Charter of Paris for a New Europe that was signed in 1990 had a statement about freedom of association – countries could choose their allies, something that would’ve been impossible under the 1975 Helsinki Declaration. Since the Warsaw Pact was running on fumes at that point, this clause meant that NATO would be free to expand. This is the document everyone keeps referring to, even in Russia. Back in 1990, however, NATO could at least be considered a “defense” organization. The alliance and most of its members have launched a number of aggressive military campaigns since then – against the remnants of Yugoslavia, as well as in Iraq and Libya.
After a heart-to-heart chat with Lech Walesa in 1993, Boris Yeltsin signed a document where it stated that Russia “understood Poland’s plan to join NATO.” When Andrey Kozyrev, Russia’s foreign minister at the time, learned about NATO’s expansion plans in 1994, he began a bargaining process on Russia’s behalf without consulting the president. The other side took it as a sign that Russia was OK with the general concept, since it was trying to negotiate acceptable terms. In 1995, Moscow stepped on the brakes, but it was too late – the dam burst and swept away any reservations about the West’s expansion efforts.
In 1997, Russia, being economically weak and completely dependent on the West, signed the Founding Act on Mutual Relations, Cooperation and Security with NATO. Moscow was able to compel certain concessions from the West, like the pledge not to deploy large military units to the new member states. NATO has been consistently violating this obligation. Another agreement was to keep these territories free of nuclear weapons. The US would not have wanted it anyway, because it had been trying to distance itself from a potential nuclear conflict in Europe as much as possible (despite their allies’ wishes), since it would undoubtedly cause a nuclear strike against America. In reality, the document legitimized NATO’s expansion.
There were other mistakes – not as major but extremely painful nevertheless. Russia participated in the Partnership for Peace program, the sole purpose of which was to make it look like NATO was prepared to listen to Moscow, but in reality, the alliance was using the project to justify its existence and further expansion. Another frustrating misstep was our involvement in the NATO-Russia Council after the Yugoslavia aggression. The topics discussed at that level desperately lacked substance. They should’ve focused on the truly significant issue – restraining the alliance’s expansion and the buildup of its military infrastructure near the Russian borders. Sadly, this never made it to the agenda. The Council continued to operate even after the majority of NATO members started a war in Iraq and then Libya in 2011.
It is very unfortunate that we never got the nerve to openly say it – NATO had become an aggressor that committed numerous war crimes. This would’ve been a sobering truth for various political circles in Europe, like in Finland and Sweden for example, where some are considering the advantages of joining the organization. And all the others for that matter, with their mantra about NATO being a defense and deterrence alliance that needs to be further consolidated so it can stand against imaginary enemies.
I understand those in the West who are used to the existing system that allows the Americans to buy the obedience of their junior partners, and not just in terms of military support, while these allies can save on security expenses by selling part of their sovereignty. But what do we gain from this system? Especially now that it’s become obvious that it breeds and escalates confrontation at our western borders and in the whole world.
NATO feeds off forced confrontation, and the longer the organization exists, the worse this confrontation will be.
The bloc is a threat to its members as well. While provoking confrontation, it doesn’t actually guarantee protection. It is not true that Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty warrants collective defense if one ally is attacked. This article doesn’t say that this is automatically guaranteed. I am familiar with the history of the bloc and the discussions in America regarding its establishment. I know for a fact that the US will never deploy nuclear weapons to “protect” its allies if there is conflict with a nuclear state.
The Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) is also outdated. It is dominated by NATO and the EU that use the organization to drag out the confrontation and impose the West’s political values and standards on everyone else. Fortunately, this policy is becoming less and less effective. In the mid-2010s I had the chance to work with the OSCE Panel of Eminent Persons (what a name!), which was supposed to develop a new mandate for the organization. And if I had my doubts about the OSCE’s effectiveness before that, this experience convinced me that it is an extremely destructive institution. It’s an antiquated organization with a mission to preserve things that are obsolete. In the 1990s, it served as an instrument of burying any attempt made by Russia or others to create a common European security system; in the 2000s, the so-called Corfu Process bogged down Russia’s new security initiative.
Practically all UN institutions have been squeezed out of the continent, including the UN Economic Commission for Europe, its Human Rights Council and Security Council. Once upon a time, the OSCE was viewed as a useful organization that would promote the UN system and principles in a key subcontinent. That didn’t happen.
As for NATO, it is very clear what we should do. We need to undermine the bloc’s moral and political legitimacy and refuse any institutional partnership, since its counterproductivity is obvious. Only the military should continue to communicate, but as an auxiliary channel that would supplement dialogue with the DOD and defense ministries of leading European nations. After all, it’s not Brussels that makes strategically important decisions.
The same policy could be adopted when it comes to the OSCE. Yes, there is a difference, because even though this is a destructive organization, it never initiated any wars, destabilization, or killings. So we need to keep our involvement in this format to a minimum. Some say that this is the only context that provides the Russian foreign minister with a chance to see his counterparts. That is not true. The UN can offer an even better context. Bilateral talks are much more effective anyway, because it is easier for the bloc to hijack the agenda when there is a crowd. Sending observers and peacekeepers through the UN would also make a lot more sense.
The limited article format does not allow me to dwell on specific policies for each European organization, like the Council of Europe for example. But I would define the general principle this way – we partner where we see benefits for ourselves and keep our distance otherwise.
Thirty years under the current system of European institutions proved that continuing with it would be detrimental. Russia doesn’t benefit in any way from Europe’s disposition towards breeding and escalating confrontation or even posing military threat to the subcontinent and the whole world. Back in the day, we could dream that Europe would help us bolster security, as well as political and economic modernization. Instead, they are undermining security, so why would we copy the West’s dysfunctional and deteriorating political system? Do we really need these new values that they have adopted?
We will have to limit the expansion by refusing to cooperate within an eroding system. Hopefully, by taking a firm stand and leaving our civilization neighbors from the West to their own devices, we will actually help them. The elites may return to a less suicidal policy that would be safer for everyone. Of course, we have to be smart about taking ourselves out of the equation and make sure to minimize the collateral damage that the failing system will inevitably cause. But maintaining it in its current form is simply dangerous.
Policies for tomorrow’s Russia
As the existing global order continues to crumble, it seems that the most prudent course for Russia would be to sit it out for as long as possible – to take cover within the walls of its ‘neo-isolationist fortress’ and deal with domestic matters. But this time, history demands that we take action. Many of my suggestions with respect to the foreign policy approach I have tentatively called ‘constructive destruction’ naturally emerge from the analysis presented above.
There is no need to interfere or to try to influence the internal dynamics of the West, whose elites are desperate enough to start a new cold war against Russia. What we should do instead is use various foreign policy instruments – including military ones – to establish certain red lines. Meanwhile, as the Western system continues to steer towards moral, political, and economic degradation, non-Western powers (with Russia as a major player) will inevitably see their geo-political, geo-economic and geo-ideological positions strengthen.
Our Western partners predictably try to squelch Russia’s calls for security guarantees and take advantage of the ongoing diplomatic process in order to extend the lifespan of their own institutions. There is no need to give up dialogue or cooperation in matters of trade, politics, culture, education, and healthcare, whenever it’s useful. But we must also use the time we’ve got to ramp up military-political, psychological, and even military-technical pressure – not so much on Ukraine, whose people have been turned into cannon fodder for a new Cold War – but on the collective West, in order to force it to change its mind and step back from the policies it has pursued for the past several decades. There is nothing to fear about the confrontation escalating: We saw tensions grow even as Russia was trying to appease the Western world. What we should do is prepare for a stronger pushback from the West; also, Russia should be able to offer the world a long-term alternative – a new political framework based on peace and cooperation.
The West can try to intimidate us with devastating sanctions – but we are also capable of deterring the West with our own threat of an asymmetrical response, one that would cripple Western economies and disrupt whole societies.
Naturally, it is useful to remind our partners, from time to time, that there exists a mutually beneficial alternative to all that.
If Russia carries out reasonable but assertive policies (domestically, too), it will successfully (and relatively peacefully) overcome the latest surge of Western hostility. As I have written before, we stand a good chance of winning this Cold War.
What also inspires optimism is Russia’s own past record: We have more than once managed to tame the imperial ambitions of foreign powers – for our own good, and for the good of humanity, as a whole. Russia was able to transform would-be empires into tame and relatively harmless neighbors: Sweden after the Battle of Poltava, France after Borodino, Germany after Stalingrad and Berlin.
We can find a slogan for the new Russian policy toward the West in a verse from Alexander Blok’s ‘The Scythians’, a brilliant poem that seems especially relevant today: “Come join us, then! Leave war and war’s alarms, / And grasp the hand of peace and amity. / While still there’s time, Comrades, lay down your arms! / Let us unite in true fraternity!”
While attempting to heal our relations with the West (even if that requires some bitter medicine), we must remember that, while culturally close to us, the Western world is running out of time – in fact, it has been for two decades now. It is essentially in damage control mode, seeking cooperation whenever possible. The real prospects and challenges of our present and future lie with the East and the South. Taking a harder line with Western nations must not distract Russia from maintaining its pivot to the East. And we have seen this pivot slow down in the past two or three years, especially when it comes to developing territories beyond the Ural Mountains.
We must not allow Ukraine to become a security threat to Russia. That said, it would be counterproductive to spend too many administrative and political (not to mention economic) resources on it. Russia must learn to actively manage this volatile situation, keep it within limits. Most of Ukraine has been neutered by its own anti-national elite, corrupted by the West, and infected with the pathogen of militant nationalism.
It would be much more effective to invest in the East, in the development of Siberia. By creating favorable working and living conditions, we will attract not only Russian citizens, but also people from the other parts of the former Russian Empire, including the Ukrainians. The latter have, historically, contributed a great deal to the development of Siberia.
Let me reiterate a point from my other articles: It was the incorporation of Siberia under Ivan the Terrible that made Russia a great power, not the accession of Ukraine under Aleksey Mikhaylovich, known under the moniker ‘the most peaceful’. It is high time we stopped repeating Zbigniew Brzezinski’s disingenuous – and so strikingly Polish – assertion that Russia cannot be a great power without Ukraine. The opposite is much closer to the truth: Russia cannot be a great power when it is burdened by an increasingly unwieldy Ukraine – a political entity created by Lenin which later expanded westward under Stalin.
The most promising path for Russia lies with the development and strengthening of ties with China. A partnership with Beijing would multiply the potential of both countries many times over. If the West carries on with its bitterly hostile policies, it wouldn’t be unreasonable to consider a temporary five-year defense alliance with China. Naturally, one should also be careful not to get ‘dizzy with success’ on the China track, so as not to return to the medieval model of China’s Middle Kingdom, which grew by turning its neighbors into vassals. We should help Beijing wherever we can to keep it from suffering even a momentary defeat in the new Cold War unleashed by the West. That defeat would weaken us, too. Besides, we know all too well what the West transforms into when it thinks it is winning. It took some harsh remedies to treat America’s hangover after it got drunk with power in the 1990s.
Clearly, an East-oriented policy must not focus solely on China. Both the East and the South are on the rise in global politics, economics, and culture, which is partly due to our undermining of the West’s military superiority – the primary source of its 500-year hegemony.
When the time comes to establish a new system of European security to replace the dangerously outdated existing one, it must be done within the framework of a greater Eurasian project. Nothing worthwhile can be born out of the old Euro-Atlantic system.
It is self-evident that success requires the development and modernization of the country’s economic, technological, and scientific potential – all pillars of a country’s military power, which remains the backbone of any nation’s sovereignty and security. Russia cannot be successful without improving the quality of life for the majority of its people: This includes overall prosperity, healthcare, education, and the environment.
The restriction of political freedoms, which is inevitable when confronting the collective West, must by no means extend to the intellectual sphere. This is difficult, but achievable. For the talented, creatively-minded part of the population who are ready to serve their country, we must preserve as much intellectual freedom as possible. Scientific development through Soviet-style ‘sharashkas’ (research and development laboratories operating within the Soviet labor camp system) is not something that would work in the modern world. Freedom enhances the talents of Russian people, and inventiveness runs in our blood. Even in foreign policy, the freedom from ideological constraints that we enjoy offers us massive advantages compared to our more close-minded neighbors. History teaches us that the brutal restriction of freedom of thought imposed by the Communist regime on its people led the Soviet Union to ruin. Preserving personal freedom is an essential condition for any nation’s development.
If we want to grow as a society and be victorious, it is absolutely vital that we develop a spiritual backbone – a national idea, an ideology that unites and shines the way forward. It is a fundamental truth that great nations cannot be truly great without such an idea at their core. This is part of the tragedy that happened to us in the 1970s and 1980s. Hopefully, the resistance of the ruling elites to the advancement of a new ideology, rooted in the pains of the communist era, is beginning to fade. Vladimir Putin’s speech at the October 2021 annual meeting of the Valdai Discussion Club was a powerful reassuring signal in that respect.
Like the ever-growing number of Russian philosophers and authors, I have put forward my own vision of the ‘Russian idea’[3]. (I apologize for having to reference my own publications again – it is an inevitable side effect of having to stick to the format).
Questions for the future
And now let’s discuss a significant, yet mostly overlooked aspect of the new policy that needs to be addressed. We need to dismiss and reform the obsolete and often harmful ideological foundation of our social sciences and public life for this new policy to get implemented, let alone succeed.
This doesn’t mean we have to reject once again the advancements in political science, economy, and foreign affairs of our predecessors. The Bolsheviks tried to dump the social ideas of tsarist Russia – everybody knows how this played out. We rejected Marxism and were happy about it. Now, fed up with other tenets, we realize we were too impatient with it. Marx, Engels, and Lenin had sound ideas in their theory of imperialism we could use.
Social sciences that study the ways of public and private life have to take into account national context, however inclusive it wants to appear. It stems from the national history and ultimately is aimed to help the nations and/or their government and elites. The mindless application of solutions valid in one country to another are fruitless and only create abominations.
We need to start working towards intellectual independence after we achieve military security and political and economic sovereignty. In the new world, it’s compulsory to achieve development and exert influence. Mikhail Remizov, a prominent Russian political scientist, was the first, as far as I know, to call this ‘intellectual decolonization’.
Having spent decades in the shadow of imported Marxism, we’ve begun a transition to yet another foreign ideology of liberal democracy in economics and political science and, to certain extent, even in foreign policy and defense. This fascination has done us no good – we’ve lost land, technology, and people. In the mid-2000s, we started to exercise our sovereignty, but had to rely on our instincts rather than clear national (again – it cannot be anything else) scientific and ideological principles.
We still don’t have the courage to acknowledge that the scientific and ideological worldview we’ve had for the last forty to fifty years is obsolete and/or was intended to serve foreign elites.
To illustrate this point, here are a few randomly picked questions from my very long list.
I’ll start with existential issues, purely philosophical ones. What comes first in humans, the spirit or the matter? And in the more mundane political sense – what drives people and states in the modern world? To common Marxists and liberals, the answer is the economy. Just remember that until recently Bill Clinton’s famous “It’s the economy, stupid” was thought to be an axiom. But people seek something greater when the basic need for food is satisfied. Love for their family, their homeland, desire for national dignity, personal freedoms, power, and fame. The hierarchy of needs has been well known to us since Maslow introduced it in the 1940–50s in his famous pyramid. Modern capitalism, however, twisted it, forcing ever-expanding consumption via traditional media at first and all-encompassing digital networks later – for rich and poor, each according to their ability.
What can we do when the modern capitalism deprived of moral or religious foundations incites limitless consumption, breaking down moral and geographic boundaries and comes into conflict with nature, threatening the very existence of our species? We, Russians, understand better than anybody that attempts to get rid of entrepreneurs and capitalists who are driven by the desire to build wealth will have disastrous consequences for society and the environment (the socialist economy model wasn’t exactly environmentally friendly).
What do we do with the latest values of rejecting history, your homeland, gender, and beliefs, as well as aggressive LGBT and ultra-feminist movements? I respect the right to follow them, but I think they’re post-humanist. Should we treat this as just another stage of social evolution? I don’t think so. Should we try to ward it off, limit its spread, and wait till society lives through this moral epidemic? Or should we actively fight it, leading the majority of humanity that adheres to so-called “conservative” values or, to put it simply, normal human values? Should we get into the fight escalating an already dangerous confrontation with the Western elites?
The technological development and increased labor productivity have helped feed the majority of people, but the world itself has slipped into anarchy, and many guiding principles have been lost at the global level. Security concerns, perhaps, are prevailing over the economy once again. Military instruments and the political will might take the lead from now on.
What is military deterrence in the modern world? Is it a threat to cause damage to national and individual assets or foreign assets and information infrastructure to which today’s Western elites are tied so closely? What will become of the Western world if this infrastructure is brought down?
And a related question: What is strategic parity we still talk about today? Is it some foreign nonsense picked by Soviet leaders who sucked their people into an exhausting arms race because of their inferiority complex and June 22, 1941 syndrome? Looks like we are already answering this question, even though we still churn out speeches about equality and symmetrical measures.
And what is this arms control many believe to be instrumental? Is it an attempt to restrain the expensive arms race beneficial to the wealthier economy, to limit the risk of hostilities or something more – a tool to legitimize the race, the development of arms, and the process of unnecessary programs on your opponent? There’s no obvious answer to that.
But let’s go back to the more existential questions.
Is democracy really the pinnacle of political development? Or is it just another tool that helps the elites control society, if we are not talking about Aristotle’s pure democracy (which also has certain limitations)? There are many tools that come and go as society and conditions change. Sometimes we abandon them only to bring them back when the time is right and there’s external and internal demand for them. I’m not calling for boundless authoritarianism or monarchy. I think we have already overdone it with centralization, especially at the municipal government level. But if this is just a tool, shouldn’t we stop pretending that we strive for democracy and put it straight – we want personal freedoms, a prosperous society, security, and national dignity? But how do we justify power to the people then?
Is the state really destined to die off, as Marxists and liberal globalists used to believe, as they dreamed of alliances between transnational corporations, international NGOs (both have been going through nationalization and privatization), and supranational political bodies? We’ll see how long the EU can survive in its current form. Note that I don’t want to say there’s no reason to join national efforts for the greater good, like bringing down expensive custom barriers or introducing joint environmental policies. Or isn’t it better to focus on developing your own state and supporting neighbors while disregarding global problems created by others? Aren’t they going to mess with us if we act this way?
What is the role of land and territories? Is it a dwindling asset, a burden as was believed among political scientists only recently? Or the greatest national treasure, especially in the face of the environmental crisis, climate change, the growing deficit of water and food in some regions and the total lack of it in others?
What should we do then with hundreds of millions of Pakistanis, Indians, Arabs, and others whose lands might soon be uninhabitable? Should we invite them now as the US and Europe began to do in the 1960s, drawing migrants to bring down the cost of local labor and undermine the trade unions? Or should we prepare to defend our territories from the outsiders? In that case, we should abandon all hope to develop democracy, as Israel’s experience with its Arab population shows.
Would developing robotics, which is currently in a sorry state, help compensate for the lack of workforce and make those territories livable again? What is the role of indigenous Russian people in our country, considering their number will inevitably keep shrinking? Given that Russians have historically been an open people, the prospects might be optimistic. But so far it’s unclear.
I can go on and on, especially when it comes to the economy. These questions need to be asked and it’s vital to find answers as soon as possible in order to grow and come out on top. Russia needs a new political economy – free from Marxist and liberal dogmas, but something more than the current pragmatism our foreign policy is based on. It must include forward-oriented idealism, a new Russian ideology incorporating our history and philosophical traditions. This echoes the ideas put forward by the academic Pavel Tsygankov.
I believe that this is the ultimate goal of all our research in foreign affairs, political science, economics and philosophy. This task is beyond difficult. We can continue contributing to our society and our country only by breaking our old thinking patterns. But to end on an optimistic note, here’s a humorous thought: Isn’t it time to recognize that the subject of our studies – foreign affairs, domestic policies, and the economy – is the result of a creative process involving masses and leaders alike? To recognize that it is, in a way, art? To a large degree, it defies explanation and stems from intuition and talent. And so we are like art experts: We talk about it, identify trends and teach the artists – the masses and the leaders – history, which is useful to them. We often get lost in the theoretical, though, coming up with ideas divorced from reality or distorting it by focusing on separate fragments.
Sometimes we do make history: think Evgeny Primakov or Henry Kissinger. But I’d argue they didn’t care what approaches to this art history they represented. They drew upon their knowledge, personal experience, moral principles, and intuition. I like the idea of us being a type of art expert, and I believe it can make the daunting task of revising the dogmas a little easier.
By Professor Sergey Karaganov, honorary chairman of Russia’s Council on Foreign and Defense Policy, and academic supervisor at the School of International Economics and Foreign Affairs Higher School of Economics (HSE) in Moscow.
Read More